Download Manufacturing specifications.
- 7B1_DistributeWorkInProcess_V01_00_00
- 7B1_DistributeWorkInProcess_V01_01_00
- 7B1_DistributeWorkInProcess_V01_02_00
- PIP7B1_V11.00.00_DistributeWorkInProcess
- 7B2_QueryWorkInProcess_R01_00_00A
- 7B5_NotifyOfManufacturingWorkOrder_V01_00_00
- 7B5_NotifyOfManufacturingWorkOrder_V01_01_00
- 7B5_NotifyOfManufacturingWorkOrder_V01_02_00
- PIP7B5_V11.00.00_NotifyOfManufacturingWorkOrder
- PIP7B5_V11.01.00_NotifyOfManufacturingWorkOrder
- 7B6_NotifyOfManufacturingWorkOrderReply_V01_00_00
- PIP7B6_V11.00.00_NotifyOfManufacturingWorkOrderReply
- PIP7B6_V11.01.00_NotifyOfManufacturingWorkOrderReply
- 7C6_DistributeProductQualityEventData_V01_00_00
- 7C6_DistributeProductQualityEventData_V01_01_00
- PIP7C6_V11.00.00_DistributeProductQualityEventData
- PIP7C7_V11.00.00_NotifyOfSemiconductorTestData
- PIP7C7_V11.01.00_NotifyOfSemiconductorTestData
- PIP7C7_V11.02.00_NotifyOfSemiconductorTestData
- PIP7C7_V11.10.00_NotifyOfSemiconductorTestData
- PIP7C7_V11.11.00_NotifyOfSemiconductorTestData
- PIP7C8_V11.00.00_NotifyOfSemiconductorProcessData
- PIP7C8_V11.10.00_NotifyOfSemiconductorProcessData
- Cluster 7, Manufacturing, enables the exchange of design, configuration, process, quality and other manufacturing floor information to support the “Virtual Manufacturing” environment.
- PIPs for Segment 7B, Manage Manufacturing WO and WIP, enables the release, management and the exchange of factory production information.
- PIPs for Segment 7C, Distribute Manufacturing Information, distribute manufacturing information to support product improvements, downstream manufacturing, Quality and warrantee entitlement.
| PIP | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 7B1 | Distribute Work in Process | To support the process used by a product manufacturer or assembler to inform a party of product configuration status. |
| 7B2 | Query Work in Process | To support the process used (1) by a solution requestor (e.g. Customer) to query the status of a product being assembled or manufactured; and 2) by a solution provider (e.g. Manufacturer or Assembler) to return the requested information. This process is usually executed when the product status is one of the following: Assembly, Text or Fabricate. |
| 7B5 | Notify Of Manufacturing Work Order | The purpose of this PIP is to notify the seller of a work order to trigger production after a PO is issued or a contract agreement exists between trading partners. |
| 7B6 | Notify of Manufacturing Work Order Reply | The purpose of this PIP is to allow an optional response to a previous manufacturing work order request. |
| 7C6 | Distribute Product Quality Event Data | Enables partners in the manufacturing/repair supply chain to share data related to the quality of services provided. |
| 7C7 | Notify of Semiconductor Test Data | Enable foundry and assembly test partners to deliver summarized chip test data to Chip designers for data analysis. The test data includes inline test, wafer test (Sort) & module final test (Package Test). |
| 7C8 | Notify of Semiconductor Process Data | Enable foundry and other inline process partners to deliver semiconductor process data to customers and other data consumers including chip designers. |
| 7B1 | Distribute Work in Process |
|---|---|
| To support the process used by a product manufacturer or assembler to inform a party of product configuration status. |
Business Process
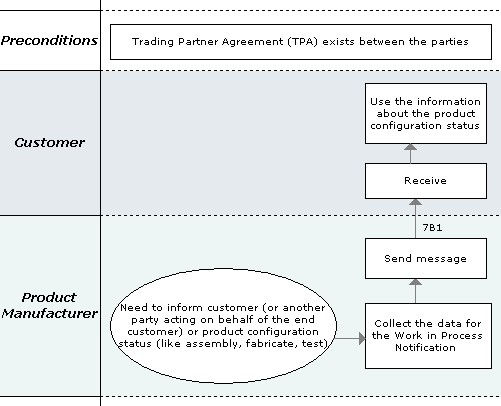
The “Distribute Work In Process” Partner Interface Process (PIP) supports the process used by a product manufacturer or assembler to inform a party of product configuration status. The recipient of the product status information could either be an end customer or another party acting on behalf of the end customer.
For example, a manufacturing subcontractor could use this PIP to inform a product supplier of product status.
This PIP is usually executed when product configuration status is one of the following:
- Assembly
- Fabricate
- Test
Should this transaction not complete successfully, the requesting partner executes PIP0A1, “Notification of Failure”.
| 7B2 | Query Work in Process |
|---|---|
| To support the process used (1) by a solution requestor (e.g. Customer) to query the status of a product being assembled or manufactured; and 2) by a solution provider (e.g. Manufacturer or Assembler) to return the requested information. This process is usually executed when the product status is one of the following: Assembly, Text or Fabricate. |
Business Process
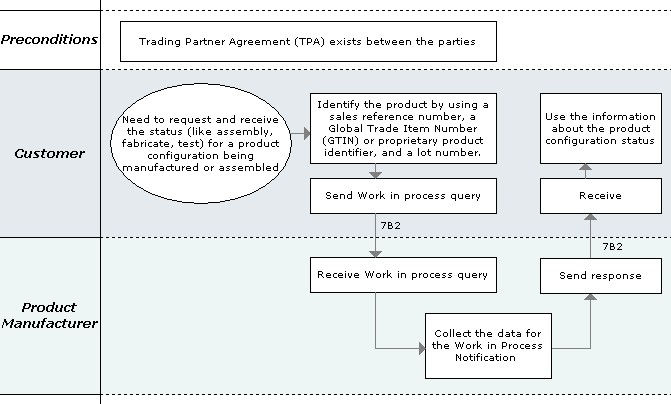
The "Query Work In Process" Partner Interface Process (PIP) supports the process used (1) by a solution requester (e. g. customer) to query the status of a product being assembled or manufactured, and (2) by a solution provider (e.g. manufacturer or assembler) to return the requested information. This process is usually executed when the product status is one of the following: Assembly, Test or Fabricate.
The solution requester initiates the process by sending a work in process query to the product solution provider. To facilitate communications, the query document includes both query constraint lines and incomplete results lines. After processing the query, the product solution provider completes the results lines and returns the information to the requesting party.
Should this transaction not complete successfully, the requesting partner executes PIP0A1, "Notification of Failure".
| 7B5 | Notify Of Manufacturing Work Order |
|---|---|
| The purpose of this PIP is to notify the seller of a work order to trigger production after a PO is issued or a contract agreement exists between trading partners. |
Business Process
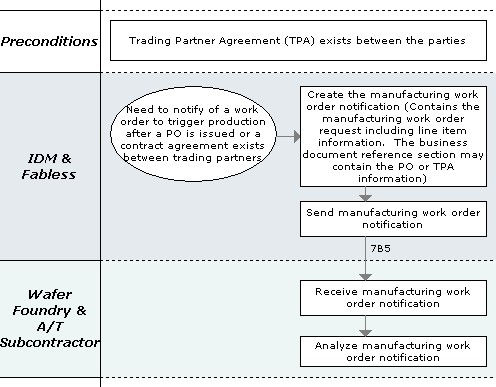
The Work Order Management Program focuses on the use of work order instructions to trigger a variety of manufacturing processes by contract manufacturers. Work orders are dependent on having a Purchase Order or by other contractual agreement, such as a Trading Partner Agreement, in place between trading partners before creating and transmitting a work order. The contractual agreements are referenced only, they are not included as part of the PIP.
This program scope includes Semiconductor Manufacturing (SM), Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEM) and Electronic Components (EC) work orders. The process deals with issuing work instructions for shop floor manufacturing of semiconductors; build requests for IT products where the products to be built have been contractually agreed to; and the dispatch of work orders for hardware final assembly and test between Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs); Fabless Semiconductor Design; and Foundry Fab/Sort/Assembly/Test Contract Manufacturers (CM). These instructions are used as authorization to process work for the requesting company.
Specifically, semiconductor companies have adopted outsourcing as the manufacturing strategy for many of the same reasons that other industries have evolved to. For example, in a Fabless Semiconductor Company the outsourcing of silicon wafers allows semiconductor companies to focus on design and marketing of its product without the burden of building, operating and upgrading manufacturing facilities. As the cost of building a wafer fabrication plant and maintenance of leading-edge process technology escalates, the fabless model is an attractive long-term option for many semiconductor companies.
An IDM or OEM will typically choose to outsource selected products or processes to a CM with the intent of augmenting capacity for the same reasons.
Should this transaction not complete successfully, the requesting partner executes PIP0A1, "Notification of Failure".
| 7B6 | Notify of Manufacturing Work Order Reply |
|---|---|
| The purpose of this PIP is to allow an optional response to a previous manufacturing work order request. |
Business Process
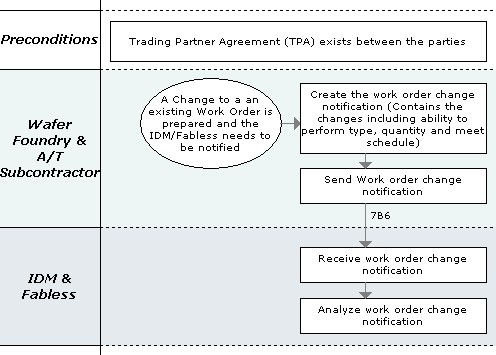
The Work Order Management Program focuses on the use of work order instructions to trigger a variety of manufacturing processes by contract manufacturers. Work orders are dependent on having a Purchase Order or by other contractual agreement, such as a Trading Partner Agreement, in place between trading partners before creating and transmitting a work order. The contractual agreements are referenced only, they are not included as part of the PIP.
This program scope includes Semiconductor Manufacturing (SM), Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEM) and Electronic Components (EC) work orders. The process deals with issuing work instructions for shop floor manufacturing of semiconductors; build requests for IT products where the products to be built have been contractually agreed to; and the dispatch of work orders for hardware final assembly and test between Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs); Fabless Semiconductor Design; and Foundry Fab/Sort/Assembly/Test Contract Manufacturers (CM). These instructions are used as authorization to process work for the requesting company.
Specifically, semiconductor companies have adopted outsourcing as the manufacturing strategy for many of the same reasons that other industries have evolved to. For example, in a Fabless Semiconductor Company the outsourcing of silicon wafers allows semiconductor companies to focus on design and marketing of its product without the burden of building, operating and upgrading manufacturing facilities. As the cost of building a wafer fabrication plant and maintenance of leading-edge process technology escalates, the fabless model is an attractive long-term option for many semiconductor companies.
An IDM or OEM will typically choose to outsource selected products or processes to a CM with the intent of augmenting capacity for the same reasons.
Should this transaction not complete successfully, the requesting partner executes PIP0A1, "Notification of Failure".
| 7C6 | Distribute Product Quality Event Data |
|---|---|
| Enables partners in the manufacturing/repair supply chain to share data related to the quality of services provided. |
Business Process
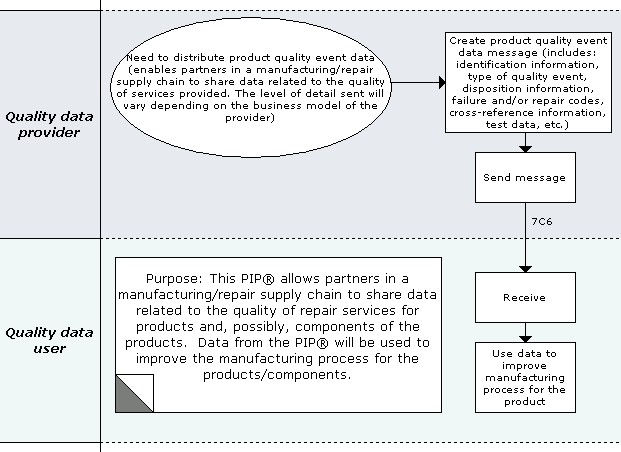
Vertically integrated companies keep track of data dealing with various quality events (e.g., product/component failures and repairs, failure analysis, etc.) on internal systems. Now that many companies outsource their manufacturing and/or repair processes, it is critical for partners to establish ways of making their quality event data available to one another.
The purpose of the "Distribute Product Quality Event Data" Partner Interface Process (PIP) is to enable partners in a manufacturing/repair supply chain to share data related to the quality of services provided.
There are two roles for this PIP: Quality Data Provider (Provider) and Quality Data User (User). The same business entity may perform either role at different stages of the manufacturing/repair supply chain - i.e., a Provider of data for a high level product could become a user of data on a component it sends out for repair or analysis.
- The Provider sends data to the User dealing with product defect(s) and/or other quality events. Quality events could occur while manufacturing the product or after the product has been sold to the end customer. For purposes of this PIP, a "product" is defined to be the physical object sent to the business partner, in its entirety. A product may have component parts that may also be reported on in the PIP
- The level of detail sent in the PIP will vary depending on the business model of the Provider. For each product:
- Identification information is provided
- The type of quality event is specified- Product received event- Repair event- Analysis event- Other business-specific events
- Disposition information (received, repaired, replaced, etc.) is provided
- Product repaired event
- Product replaced event- Product scrapped event
- Other business-specific disposition events
- Failure and/or repair codes are provided
- Cross-reference information may be provided to associate the product with other business documents (e.g., purchase orders, sales orders, etc.) and/or to associate the product with its component parts (see the next paragraph and its discussion on "Master Event Number")
- Test data (e.g., type of tests performed, variables tested for, attribute and parametric test results, etc.) may be provided Components that are repaired, replaced, or updated are identified along with their defect and/or repair codes and, optionally, their test data
- The User aggregates and uses the data according to its business model - e.g., to improve the quality of its manufacturing operations.
It may be necessary to send a component of a product to a partner for repair/analysis. If this happens, the component takes on the role of "product" in a new instance of the PIP, with the Provider becoming the User and the new business entity becoming the Provider. Products and components are linked together across PIPs by way of a "Master Event Number", thus allowing the original product vendor to aggregate data regardless of the number of business entities involved. The Master Event Number is one example of cross-reference information that may be included in the PIP.
It is also possible, for a PIP to be sent to any "upstream" partner (assuming, of course, there is an agreement in place between the business entities).This PIP does not specify turnaround times or other details of how the Provider carries out its repair business. These operational aspects are determined by the Provider's business model and agreements between the Provider and User.
Should this transaction not complete successfully, the requesting partner executes PIP0A1, "Notification of Failure".
| 7C7 | Notify of Semiconductor Test Data |
|---|---|
| Enable foundry and assembly test partners to deliver summarized chip test data to Chip designers for data analysis. The test data includes inline test, wafer test (Sort) & module final test (Package Test). |
Business Process
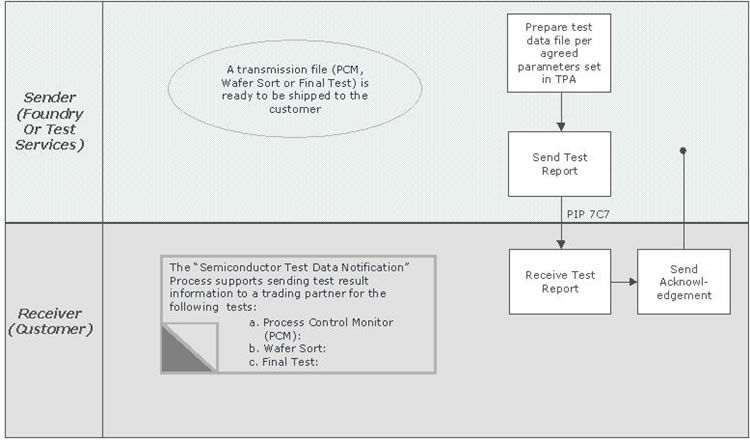
The “Semiconductor Test Data Notification” Partner Interface Process supports the process to send test result information to a trading partner for the following semiconductor tests:
- Process Control Monitor (PCM): The data resulting from the testing of a sample of chips on a semiconductor wafer to determine if chips meet engineering specifications. For a foundry environment, this test data provides the ‘go’ or ‘no go’ decision to determine if the wafer passes or fails the agreed upon wafer acceptance criteria. This test data is limited to data produced from testing individually wired devices / structures built in the “dicing channel”, “kerf” or “scribe line” versus the functional / integrated die on the entire wafer.
- Wafer Sort: The data resulting from the functional testing for each functional / integrated die on the entire wafer. The test data results may be shared as either reconciled information at the chip summary level or as raw test data. Test results may include parametric measurements and quality sort data.
- Final Test: The data resulting from the testing of packaged die to ensure functionality of the die encapsulated package. This test also includes parametric and quality sort data.
Should this transaction not complete successfully, the requesting partner executes PIP0A1, "Notification of Failure".
| 7C8 | Notify of Semiconductor Process Data |
|---|---|
| Enable foundry and other inline process partners to deliver semiconductor process data to customers and other data consumers including chip designers. |
Business Process
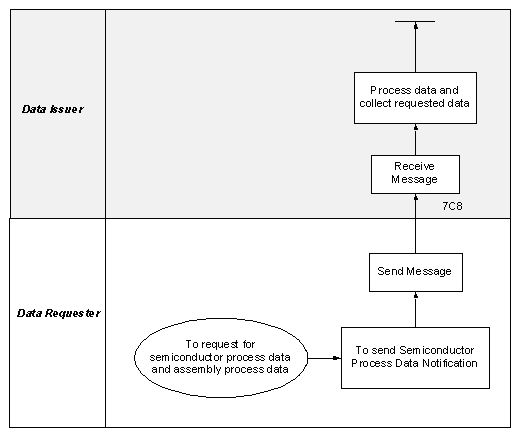
The “Semiconductor Test Data Notification” Partner Interface Process supports the process to send test result information to a trading partner for the following semiconductor tests:
- Process Control Monitor (PCM): The data resulting from the testing of a sample of chips on a semiconductor wafer to determine if chips meet engineering specifications. For a foundry environment, this test data provides the ‘go’ or ‘no go’ decision to determine if the wafer passes or fails the agreed upon wafer acceptance criteria. This test data is limited to data produced from testing individually wired devices / structures built in the “dicing channel”, “kerf” or “scribe line” versus the functional / integrated die on the entire wafer.
- Wafer Sort: The data resulting from the functional testing for each functional / integrated die on the entire wafer. The test data results may be shared as either reconciled information at the chip summary level or as raw test data. Test results may include parametric measurements and quality sort data.
- Final Test: The data resulting from the testing of packaged die to ensure functionality of the die encapsulated package. This test also includes parametric and quality sort data.
Should this transaction not complete successfully, the requesting partner executes PIP0A1, "Notification of Failure".
