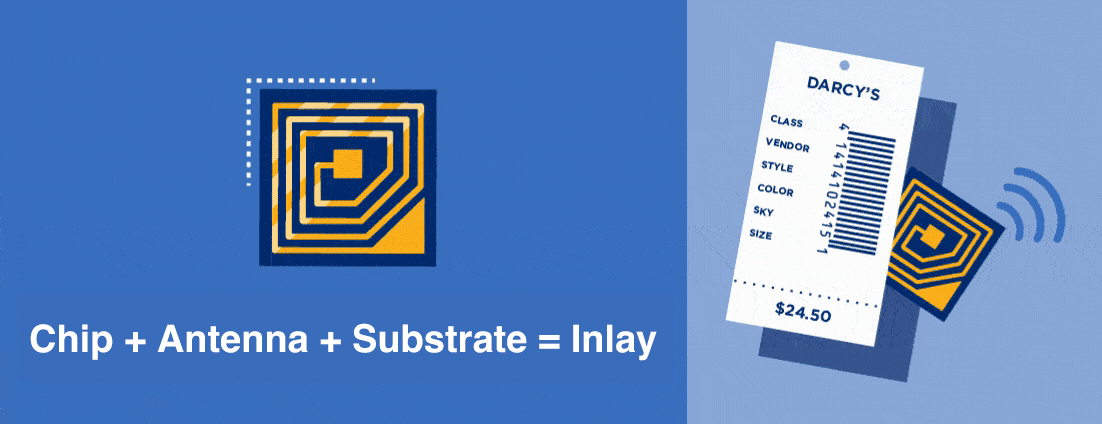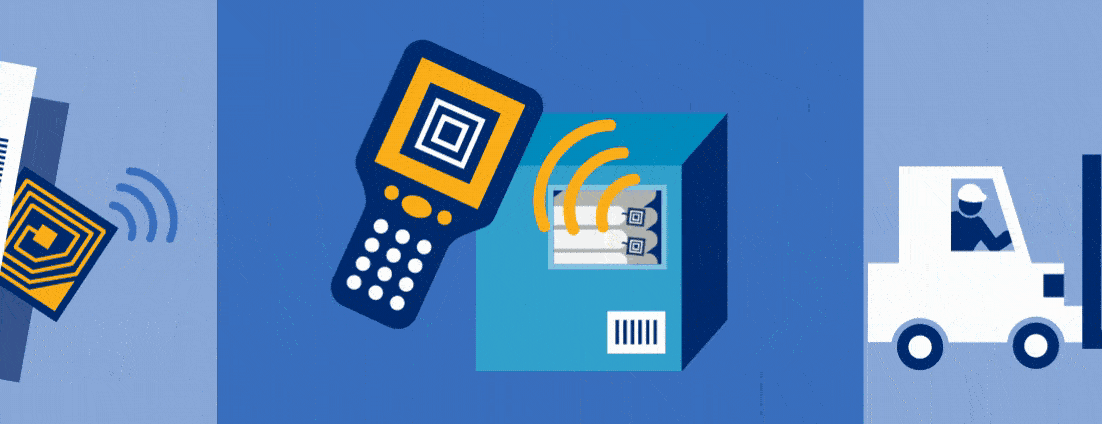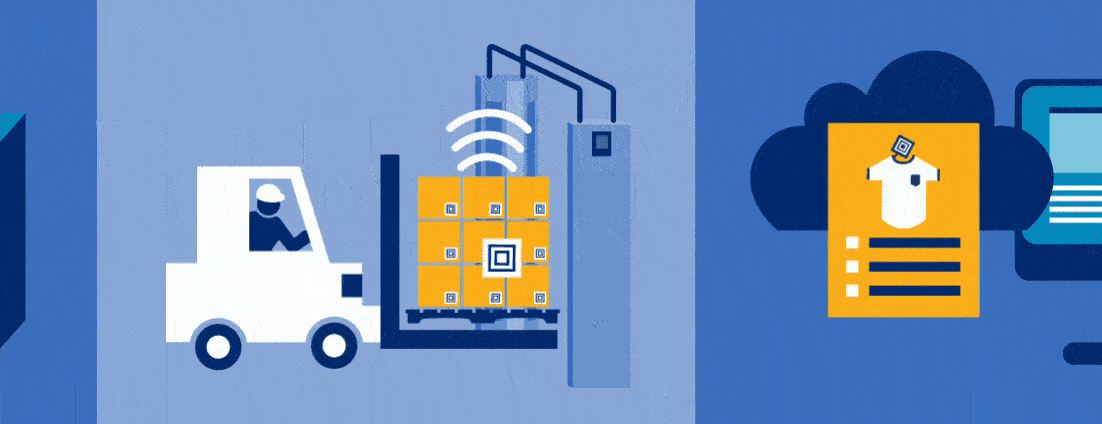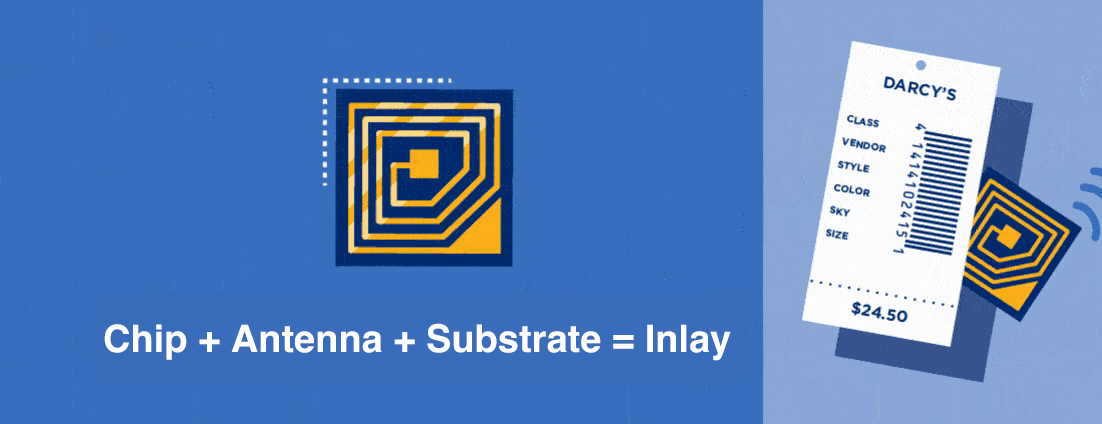
RFID technology has evolved for various uses. It can handle simple tasks like locating your remote control. RFID technology can also handle detailed tasks such as warehouse inventory management, unlocking hotel rooms, and tracking patients in hospitals. The applications of this technology are endless.
If you’re considering implementing RFID technology in your company, you might wonder, “What is RFID technology?” and “How does RFID work?” We can provide examples to explain both and weigh the pros and cons of integrating this technology into your business.